Information and System Classification
Kriterien zur Kategorisierung, Gruppierung und Filterung von Informationssystemen und IT-Diensten
Unter Klassifizierung im Kontext von Information-Management und der Informationssicherheit versteht man den Prozess der Kategorisierung institutioneller Informationen und IT-Ressourcen auf der Grundlage ihrer Sensibilität und Kritikalität sowie der potenziellen Auswirkungen, falls ihre Vertraulichkeit, Integrität oder Verfügbarkeit gefährdet sein sollte. Der Prozess wird in der Regel durch rechtliche, behördliche, finanzielle und betriebliche Anforderungen bestimmt. Die Klassifizierung eines Vermögenswerts (Assets) oder IT-Dienstes hilft dabei, die grundlegenden Sicherheitskontrollen zu bestimmen, die zum Schutz des Vermögenswerts implementiert werden sollten
Klassifzierung von IT-Services nach Titel
Die IT-Services werden nach ihrem Titel oder ihrer Bezeichnung gruppiert und sortiert. IT-Services von A bis Z.
Klassifzierung von IT-Services nach Benutzergruppen oder Rollen
Der Fokus bei der benutzerrollenorientierte Klassifizierung liegt im Nutzungskontext der Benutzer und derer Bedürfnissen und den ihnen zugewiesenen Rollen.Mit dieser Sicht soll eine hoheÜbersichtlichkeit und Benutzerfreundlichkeit sichergestellt werden. Die häufig der verwendete IT-Services und Gelegenheitsdienste. (Heat-Maps, Analytics-Auswertungen) kann hier bei der Sortierung helfen.
- IT-Services für Mitarbeiter (Basis-Dienste)
- IT-Services für Projektmanagement-Mitarbeiter
- IT-Services für Prozessmanagement-Mitarbeiter
- IT-Services für IT-Mitarbeiter
- ...
Klassifzierung von IT-Services nach Servicetypen - Servicebereichen
IT-Services können nach ihrem Typ und ihrer thematisch oder funktional Art klassifiziert werden. Das IT-Referenzmodell ITIL verwendet hierzu:
- IT-TS - IT-Technical-Services
- IT-BS - IT-Business-Services und
- IT-PS - IT-Dienstleistungen (Professional Services, Prozesse aus der IT-Prozesslandkarte, Helpdesk, Vor-Ort-Support, Beratung).
Die Kategorien werden nach IT-Servicereichen (Domains), IT-Servicegebieten (Areas) und IT-Servicegruppen (Groups) gruppiert und damit hierarchisch gegliedert.
Klassifzierung von IT-Services nach OEs oder Geschäftsprozessen
Der Fokus bei der prozessorientierte Klassifizierung liegt im Kontext von Tätigkeiten und Prozessnutzung. Der Katalog wird basierend auf den Anwendungsszenarien und Geschäftsprozesse klassifiziert, wie etwa
- nach Aufbauorgansition - OEs (Abteilungen wie Vertrieb, Controlling) oder
- nach Ablauforganisation - Geschäftsprozesse (GP fpr Projektmanagement, GP für SCM-Produktion, GP für CRM, ... ).
Die Klassifizierungsparameter stammen idR. von einem BPM-Repository.
Klassifzierung von IT-Services nach Serviceausprägungen
IT-Service haben idR. verschiedene Ausprägungen bei Attributen. Diese Attribute dienen zu weiteren Klassifizierung. Diese Ausprägungen können hierarchisch oder tabellarisch dargestellt werden, wie etwa Verfügbarkeitsklassen, nach Risiko-Einstufungen (BIA-Analyse), nach SLAs, nach Kostenumfang (TCO-Klassen). nach Verantwortlichkeiten, Kontaktinformationen, ... Ein IT-Serviceverzeichnis nach Serviceausprägungen organisiert IT-Dienste basierend auf ihren spezifischen Eigenschaften.
Klassifzierung von IT-Services nach Verfügbarkeitsstufen - Availability Levels
siehe Availability-Levels
Klassifzierung von IT-Services nach Verfügbarkeitsklassen
siehe Verfügbarkeitsklassen
Klassifzierung von IT-Services nach Protection Level
siehe Protection-Levels - Informationsklassifizierung
Klassifzierung von IT-Services nach Severity-Level ( BIA)
Service-Severity - Kritikalität oder Wichtigkeit: Services können nach ihrer Bedeutung und der Auswirkungen eines Serviceausfalls auf das Geschäft in verschiedene Kategorien eingeteilt werden. Dies hilft bei der Ressourcenpriorisierung und -zuweisung. Die Bewertung der Bedeutung von IT-Services gemäß einem Business Impact Analysis (BIA) ist ein wesentlicher Schritt bei der Festlegung der Wiederherstellungs- und Kontinuitätsstrategien für den Fall von Störungen oder Ausfällen. Die BIA zielt darauf ab, die geschäftlichen Auswirkungen von IT-Ausfällen zu verstehen und die Priorität von IT-Services festzulegen. Diese Klassifizierung hilft bei der Priorisierung von Wiederherstellungsstrategien und Notfallmaßnahmen.
- SS-0: gering
- SS-2: mittel
- SS-3 wichtig
- SS-4: geschäftskritisch
Klassifzierung von IT-Services nach Betriebszeiten
siehe Betriebszeit
IT-Services können nach den Betriebszeiten klassifiziert werden. IT-Servicebetriebszeiten beziehen sich auf die Zeiten, während derer ein bestimmter IT-Service für Benutzer oder Kunden verfügbar ist und unterstützt wird. Diese Zeiten definieren, wann der Service aktiv und funktionsfähig ist und Benutzer darauf zugreifen können. Die IT-Servicebetriebszeiten werden oft in Service-Level-Agreements (SLAs) festgelegt, um klare Erwartungen hinsichtlich der Nutzbarkeit eines IT-Services zu schaffen.
- BZ-0 - Betrieb nach Bedarf aktiviert, keine Betriebszeiten vereinbart. Services die nur bei Bedarf benötigt werden, ZB. Analysen, Scans, ...
- BZ-24x7 - Service ist rund um die Uhr nutzbar.
- BZ-geschäftszeitenabhängig von - bis: 0 6 * * 1-5; 0 20 * * 1-5 (zu Zeitangaben siehe corn-Jobs): Start um 0600 von Mon bis Freitag bis 20h nutzbar. zB. für Kassensysteme, Alarmanlagen
- BZ-W - geplante Wartungzeiten - Zyklen
Klassifzierung von IT-Services nach Supportzeiten
siehe Supportbetriebszeiten
Services können nach den Supportzeiten klassifiziert werden. IT-Servicesupportzeiten beziehen sich auf die Zeiten, während derer ein bestimmter IT-Service von IT-Support unterstützt wird. Diese Zeiten definieren, wann der Support bereit steht. Die IT-Servicesupportzeiten werden oft in Service-Level-Agreements (SLAs) festgelegt, um klare Erwartungen hinsichtlich der Verfügbarkeit des Supports eines IT-Services zu schaffen.
- SZ-0 - keine Supportzeiten vereinbart.
- SZ-24x7 - Service ist rund um die Uhr betreut.
- SZ-geschäftszeitenabhängig von - bis: 0 6 * * 1-5; 0 20 * * 1-5 (zu Zeitangaben siehe corn-Jobs): Start um 0600 von Mon bis Freitag bis 20h nutzbar. zB. für Kassensysteme, Alarmanlagen.
Klassifzierung von IT-Services nach Nutzergruppen
Service-Nutzer: Services können nach den Benutzerbereichen und - gruppen, die sie verwenden, klassifiziert unterschieden werden. Services für
- SN-A - Alle Stakeholder: ZB. Websites, Informationsportal
- SN-K - (Unternehmens-)Kunden. ZB. Website, Webshop, ...
- SN-M - (Prozess-)Mitarbeiter. ZB. Intranet, Zeiterfassung, Reporting, Monitoring, VPN-Remote-Access, Repositories, Digital Workplace, ...
- SN-L - Lieferanten und Geschäftspartner. ZB: Ausschreibungsportale, Shared Workspaces, ...
- SN-S - ZB: Maschine2Maschine
Klassifzierung von IT-Services nach TCO
Service-Kosten: Hierbei geht es um die Kosten (TCO = Total Cost of Ownership) für die Bereitstellung und den Betrieb des Services.
- TCO-0: keine Kosten vereinbart, bekannt.
- TCO-1: niedrige Kosten (kleiner als ....)
- TCO-2 mittlere Kosten (von ... bis ...) oder
- TCO-4: hohe Kosten (größser als ....)
Klassifzierung von IT-Services nach Status
Services können nach Ihren Lebenszyklus-Status gemäß ITIL klassifiziert werden.

1. Status-P - Abschnitt Plan - Transform
- Status-P.I - Vorgeschlagen, Idee, Demand - definiert
- Status-P.A - Analysiert
- Status-P.P - Genehmigt - approved
- Status-P.C - Beauftragt - chartered
2. Status-B Abschnitt Build - Change
- Status-B.Con - Konzipiert - designed
- Status-B.Dev - Gebaut - erstellt, entwicklet, gekauft
- Status-B.Tes - Getestet
- Status-B.Rel - Freigegeben - Released
3. Status-R Abschnitt Run - Operate
- Status-R - Operational: In Betrieb - operational
4. Status-E Abschnitt EoL
- Status-EoL - End-of-Life: wird nicht mehr installiert, aber nich betrieben
- Status-EoS - End-of Servie: wird nicht mehr serviert und nicht mehr betriebn. Eingestellt - pensioniert
Klassifzierung von IT-Services nach Produktreifegrad
Services können nach Ihren Reifegrad klassifiziert werden.
- PdRG-0: keine Produktreifegrad bekannt, ermittelt.
- PdRG-1: niedrige Produktreifegrad
- PdRG-2: mittlerer Produktreifegrad
- PdRG-4: mittlerer Produktreifegrad
Klassifzierung von IT-Services nach Regionen
In multinationalen Unternehmen können Services je nach den Regionen oder Ländern, in denen sie bereitgestellt werden, klassifiziert werden.
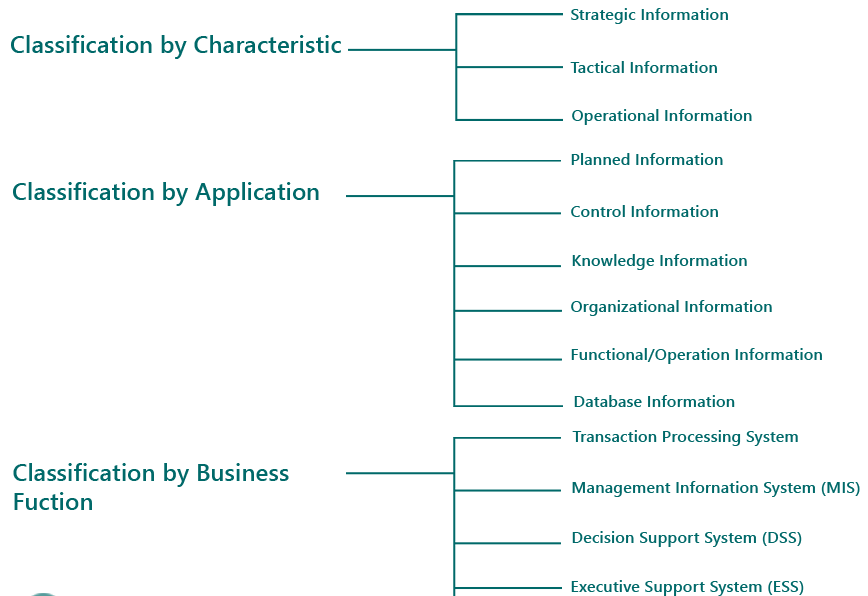
Classification as per Information Characteristics
Based on Anthony's brand of Management, information that is used in commerce trade for decision-making is generally categorized into three types:
- Strategic Information: Strategic information deals with an objective of a house with long-term policy decisions as well as checks provided these objectives are met up to their level or not. For example, acquiring the new plant, the new product, diversification of chain, etc, comes under strategic information.
- Tactical Information: Tactical information deals with the information needed to rule over business resources, like budgeting, bracket control, improvement level, stock level, productivity level, etc.
- Operational Information: Operational information deals with plant/business level information as well as is used to handle proper conduction of specific operational tasks as planned/intended. Various operators specific, machine-specific as well as shift particular jobs for quality authority checks come under this category.
Classification as per Business Function
- Transaction Processing System: TPS processes transactions and produces reports. It refers to the automation of basic, repetitive processing that underpins business operations. It does not afford any information to the user for his/her decision-making. TPS uses data and produces data as proposed in the coming after or as a result of the diagram. Previously, TPS was invited as the administration Information System. Data processing was used by manual processes or with simple machines prior to the invention of computers. The TPS domain is located at the bottom of an organization's management hierarchy.
- Management Information System (MIS): As MIS is a well-known information system to organize the information, which processes data and converts it into meaningful information. A supervision information system uses TPS for its data inputs. The information generated by the information system may live used for sources of operations, strategic and long-range planning. Short-term planning, supervision control, and other managerial problem solving encompass processing in assist of a wide range of organizational functions & management processes. MIS is capable of providing analysis, planning & decision developing support. Marketing, manufacturing, human resources, finance, and accounting are some of the functional areas of a company.
- Decision Support System (DSS): A decision help system (DSS) is an information system a formal request to be considered for a position or to be allowed to do or have something. That assists decision-making. DSS be inclined with planning, analyzing alternatives, and trial and error search for the solution. The elements of the decision support system include a database & software. Finance, Production, and marketing are some of the main application areas of DSS. Based on how information is processed, DSS can be distinguished from MIS. MIS processes data to restyle it into information. DSS processes information to support the decision creating process of a manager.
- Executive Support System (ESS): Executive Support System (ESS) is a reference of the management information system, which is a special kind of DSS; An ESS is specially tailored for the ownership of the chief executive of an association to support his decision-making. It includes various types of decision-making but it is more specific and adult-oriented.
- Office Automation Systems (OAS): Office automation is referenced to the application of computes and communication technology to office functions. Office automation systems are meant to improvements the productivity of frameworks at various levels of management by providing secretarial assistance and better communication facilities.
Classification as per Application
- Planned Information: This is the information used in business organizations maintaining specification norms and specifications. Everything is mentioned here. This information is used in the strategic, tactical, and operation planning of any activity. Examples of such information are time standards, design standards.
- Control Information: This information is termed for specific activities performed by the system in design to attain their objectives. This information might cost formal or informal. It is used for controlling attainment, line, and utilization of important processes in a system. When this information did make-up any deviation from the defining standards, the system should be imposing a decision or an action main to authority the information related to their objectives.
- Knowledge Information: cognition is defined as "information about information". Knowledge information is acquired through experience and learning and collected from archival data and research studies.
- Organizational Information: Organizational information deals with an organization's environment, where organizational objectives are met. Karl Weick's Organizational Information theory emphasizes that a company reduces its uncertainty by collecting, managing, and using this information carefully. This information is used by everybody in the organization; examples of such information are employee and payroll information.
- Functional/Operational Information: This is operation-specific information where the organization assists to perform its functions of day-day transactions. Mainly preserves technical make-up, For example, daily schedules in a manufacturing plant that indicated the detailed assignment of jobs to machines or machines to operators. In a value-oriented business, it would constitute the duty roster of various personnel. This information is mostly internal to the organization.
- Database Information: Database information as we know that it is a collection of related data that is stored, retrieved, and managed to name databases. It stores large quantities of information that has multiple ownership and application. For example, the tangible substance that goes into the makeup of physical thing specification or supplier information is stored for multiple users. It is a type of software program.